How to do long division with remainders?
When we are given a long division to do it will not always work out to a whole number. Sometimes there will be numbers left over. These are known as
remainders. Taking an example similar to that on the
Long Division page it becomes more clear: 435 ÷ 25.
If you feel happy with the process on the Long Division | 4 ÷ 25 = 0 remainder 4 | The first number of the dividend is divided by the divisor. |
 |
| The whole number result is placed at the top. Any remainders are ignored at this point. |
 | 25 × 0 = 0 | The answer from the first operation is multiplied by the divisor. The result is placed under the number divided into. |
 | 4 – 0 = 4 | Now we take away the bottom number from the top number. |
 |
| Bring down the next number of the dividend. |
 | 43 ÷ 25 = 1 remainder 18 | Divide this number by the divisor. |
 |
| The whole number result is placed at the top. Any remainders are ignored at this point. |
 | 25 × 1 = 25 | The answer from the above operation is multiplied by the divisor. The result is placed under the last number divided into. |
 | 43 – 25 = 18 | Now we take away the bottom number from the top number. |
 |
| Bring down the next number of the dividend. |
 | 185 ÷ 25 = 7 remainder 10 | Divide this number by the divisor. |
 |
| The whole number result is placed at the top. Any remainders are ignored at this point. |
 | 25 × 7 = 175 | The answer from the above operation is multiplied by the divisor. The result is placed under the number divided into. |
 | 185 – 175 = 10 | Now we take away the bottom number from the top number. |
|
| There is still 10 left over but no more numbers to bring down. |
 |
| With a long division with remainders the answer is expressed as 17 remainder 10 as shown in the diagram |
External LinkMore books about long division for kidsMathimagination Series: Book A, beginning multiplication and division; Book B, operations with whole numbers; Book C, number theory, sets and number bases; Book D, fractions; Book E, decimals and percent | Decimals and Percentages With Pre- And Post-Tests: Place Value, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division | | |
Read more




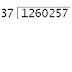



















0 comments:
Post a Comment